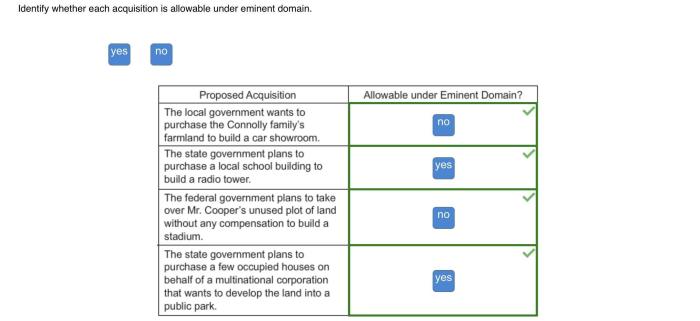
Identify whether each acquisition is allowable under eminent domain. – Identifying whether an acquisition is allowable under eminent domain requires an in-depth understanding of the legal principles governing the exercise of this governmental power. This comprehensive guide explores the various acquisition types, allowable purposes, public use requirement, just compensation, procedural requirements, and defenses to eminent domain.
By examining real-world examples and case studies, we aim to provide a clear and authoritative analysis of this complex legal landscape.
1. Acquisition Types
Eminent domain is the right of a government to take private property for public use. There are two main types of acquisitions that can be made through eminent domain:
- Fee simple acquisition:This is the most complete type of acquisition, in which the government takes full ownership of the property.
- Easement acquisition:This is a less complete type of acquisition, in which the government takes only a limited interest in the property, such as the right to use the property for a specific purpose.
2. Allowable Purposes

Eminent domain can only be used for public purposes. Some of the most common allowable purposes for eminent domain include:
- Public infrastructure:This includes roads, bridges, schools, and hospitals.
- Public utilities:This includes water, sewer, and electricity lines.
- Parks and recreation areas:This includes parks, playgrounds, and hiking trails.
- Economic development:This includes projects that are intended to create jobs and boost the economy.
Eminent domain cannot be used for private purposes, such as taking property for a private business.
3. Public Use Requirement: Identify Whether Each Acquisition Is Allowable Under Eminent Domain.
The public use requirement is one of the most important limitations on the use of eminent domain. In order for an acquisition to be valid, the government must show that the property will be used for a public purpose.
The public use requirement has been interpreted broadly by the courts. In recent years, the courts have upheld acquisitions for a variety of purposes, including economic development, historic preservation, and environmental protection.
However, the public use requirement is not without limits. The courts have struck down acquisitions that were not truly for a public purpose, such as taking property for a private business or for the sole purpose of increasing tax revenue.
4. Just Compensation

The Fifth Amendment to the United States Constitution requires that the government pay just compensation for property taken through eminent domain.
Just compensation is the fair market value of the property at the time of the taking. In determining just compensation, the courts consider a variety of factors, including the property’s location, size, and condition.
The government is not required to pay for the sentimental value of the property or for any other losses that the owner may suffer as a result of the taking.
5. Procedural Requirements
There are a number of procedural requirements that must be followed in an eminent domain acquisition.
- Notice:The government must provide the owner of the property with notice of the taking and the amount of just compensation that will be paid.
- Hearing:The owner of the property has the right to a hearing to contest the taking or the amount of just compensation.
- Payment:The government must pay the owner of the property just compensation before taking possession of the property.
Failure to follow these procedural requirements can result in the taking being invalid.
6. Defenses to Eminent Domain

There are a number of defenses that can be raised to an eminent domain acquisition.
- The taking is not for a public purpose.
- The taking is not necessary.
- The just compensation offered is not adequate.
- The procedural requirements have not been followed.
If a defense is successful, the taking will be invalid and the owner of the property will be entitled to keep their property.
FAQ
What is the public use requirement for eminent domain acquisitions?
The public use requirement mandates that property taken through eminent domain must be used for a public purpose, such as the construction of roads, schools, or parks.
What are the procedural requirements that must be followed in an eminent domain acquisition?
Procedural requirements include providing notice to the property owner, holding a public hearing, and obtaining a court order authorizing the acquisition.
What defenses can be raised to an eminent domain acquisition?
Defenses include challenging the public use requirement, the necessity of the acquisition, or the amount of just compensation offered.