A hydrogen filled balloon was ignited and 1.50g – A hydrogen-filled balloon was ignited and 1.50g of hydrogen was released, leading to a fascinating combustion reaction. This article delves into the properties of hydrogen, the combustion process, energy release, safety considerations, and applications of hydrogen combustion.
Hydrogen, a highly flammable gas, plays a crucial role in various industries and scientific advancements. Understanding its combustion characteristics is essential for harnessing its potential while mitigating associated hazards.
Hydrogen Properties
Hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant element in the universe. It is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas. Hydrogen is highly flammable and can form explosive mixtures with air. It is also a powerful reducing agent and can react with many other elements and compounds.
Physical Properties
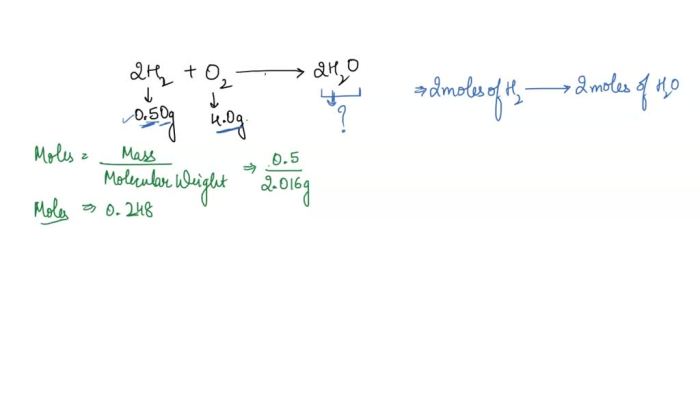
- Molecular weight: 2.016 g/mol
- Density: 0.0899 g/L
- Melting point: -259.2 °C
- Boiling point: -252.9 °C
Chemical Properties
- Hydrogen is a highly reactive element.
- It can react with many other elements to form compounds.
- Hydrogen is a powerful reducing agent.
Uses of Hydrogen
- Hydrogen is used as a fuel in rockets and fuel cells.
- It is also used in the production of ammonia, fertilizers, and plastics.
- Hydrogen can be used as a clean source of energy.
Potential Hazards of Hydrogen
- Hydrogen is a flammable gas and can form explosive mixtures with air.
- It can also cause skin irritation and respiratory problems.
- Hydrogen should be handled with care.
- The burning of natural gas
- The operation of a fuel cell
- The explosion of a hydrogen-filled balloon
- The type of fuel
- The amount of fuel
- The amount of oxygen available
- The temperature of the reaction
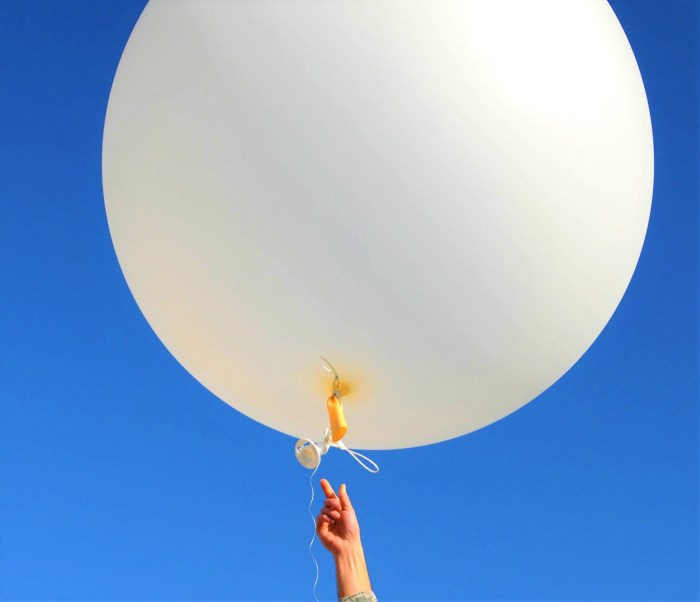
- Hydrogen-filled balloons can explode if they are ignited.
- The explosion can cause serious injuries or death.
- It is important to never ignite a hydrogen-filled balloon.
- Hydrogen should be stored in a cool, dry place.
- Hydrogen should be handled in a well-ventilated area.
- Hydrogen should never be handled near a source of ignition.
- Advantages:Hydrogen-powered vehicles are more efficient than gasoline-powered vehicles. They also produce zero emissions.
- Disadvantages:Hydrogen-powered vehicles are more expensive than gasoline-powered vehicles. They also have a shorter range than gasoline-powered vehicles.
Combustion Reaction

Combustion is a chemical reaction that involves the rapid reaction of a substance with oxygen. Hydrogen is a highly flammable gas and can easily undergo combustion. The combustion of hydrogen produces water vapor and heat.
Chemical Equation for the Combustion of Hydrogen
The chemical equation for the combustion of hydrogen is:
2H2+ O 2→ 2H 2O
Real-World Examples of Combustion Reactions Involving Hydrogen, A hydrogen filled balloon was ignited and 1.50g
Energy Release

The combustion of hydrogen releases a large amount of energy. The amount of energy released can be calculated using the following equation:
ΔH =
286 kJ/mol
Where ΔH is the change in enthalpy, or the amount of heat released, and mol is the number of moles of hydrogen that react.
Factors That Affect the Energy Output of a Combustion Reaction
Comparison of the Energy Release of Hydrogen Combustion to Other Fuels
Hydrogen has a higher energy content per unit mass than any other fuel. This means that hydrogen can produce more energy than other fuels, such as gasoline or natural gas.
Safety Considerations
Hydrogen is a flammable gas and can form explosive mixtures with air. It is important to take precautions when handling hydrogen.
Potential Hazards Associated with Igniting Hydrogen-Filled Balloons
Precautions That Should Be Taken When Handling Hydrogen
Importance of Proper Ventilation and Safety Equipment
It is important to have proper ventilation when handling hydrogen. This will help to prevent the accumulation of hydrogen in the air, which could lead to an explosion.
It is also important to wear proper safety equipment when handling hydrogen. This includes gloves, goggles, and a lab coat.
Applications of Hydrogen Combustion: A Hydrogen Filled Balloon Was Ignited And 1.50g
Hydrogen combustion has a wide range of applications, including:
Use of Hydrogen Combustion in Fuel Cells
Fuel cells are devices that convert hydrogen and oxygen into electricity. Fuel cells are used in a variety of applications, including powering vehicles and providing backup power for critical systems.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Hydrogen-Powered Vehicles
Potential Role of Hydrogen Combustion in Renewable Energy Systems
Hydrogen combustion can play a role in renewable energy systems. Hydrogen can be produced from renewable sources, such as solar and wind power. Hydrogen can then be used to generate electricity or power vehicles.
FAQ Resource
What are the hazards associated with igniting hydrogen-filled balloons?
Hydrogen is highly flammable and can explode if ignited in an enclosed space. It also produces intense heat, which can cause burns.
What precautions should be taken when handling hydrogen?
Hydrogen should be handled in well-ventilated areas, and proper safety equipment, such as gloves and goggles, should be worn. Open flames and sparks should be kept away from hydrogen sources.
What are the potential applications of hydrogen combustion?
Hydrogen combustion is used in fuel cells to generate electricity, and in hydrogen-powered vehicles. It also has potential applications in renewable energy systems, such as hydrogen-based power plants.