Welcome to the fascinating world of cell cycle labeling, where we unravel the intricate dance of cell division! With our comprehensive guide, the cell cycle labeling answers key, you’ll embark on an extraordinary journey into the heart of cellular biology, unlocking the secrets of how cells grow, divide, and repair themselves.
As we delve into the depths of cell cycle labeling, we’ll explore the various techniques used to visualize this dynamic process, discover the checkpoints that ensure its accuracy, and uncover the groundbreaking applications that are revolutionizing medical research and advancements.
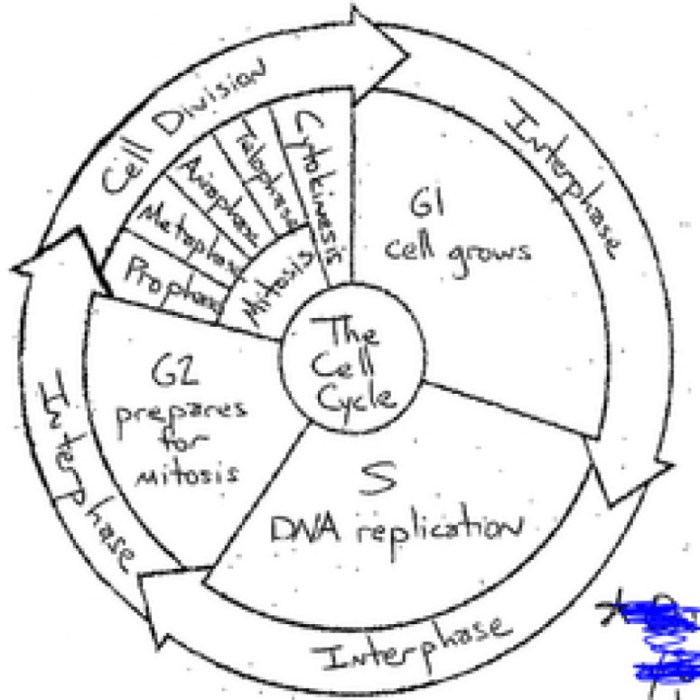
Cell Cycle Stages
The cell cycle is the process by which a cell grows and divides. It is divided into four stages: interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Interphase is the longest stage of the cell cycle and is characterized by cell growth and DNA replication.
Prophase is the stage in which the chromosomes become visible and the nuclear envelope breaks down. Metaphase is the stage in which the chromosomes line up in the center of the cell. Anaphase is the stage in which the chromosomes are separated and pulled to opposite ends of the cell.
Telophase is the stage in which two new nuclear envelopes form around the chromosomes and the cell membrane pinches in the middle, dividing the cell into two daughter cells.
Key Events and Characteristics of Each Stage
The following table summarizes the key events and characteristics of each stage of the cell cycle:
| Stage | Key Events | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Interphase | Cell growth, DNA replication | Chromosomes not visible, nuclear envelope intact |
| Prophase | Chromosomes become visible, nuclear envelope breaks down | Chromosomes condense, spindle fibers form |
| Metaphase | Chromosomes line up in the center of the cell | Spindle fibers attach to chromosomes |
| Anaphase | Chromosomes are separated and pulled to opposite ends of the cell | Spindle fibers shorten |
| Telophase | Two new nuclear envelopes form around the chromosomes, cell membrane pinches in the middle, dividing the cell into two daughter cells | Chromosomes decondense, nuclear envelope reforms |
Labeling Techniques
Labeling techniques are essential for visualizing and studying the cell cycle. They allow researchers to track individual cells as they progress through the different stages of the cycle, and to identify the proteins and other molecules that are involved in each stage.
Looking for the answers to your cell cycle labeling questions? Look no further! And while you’re at it, don’t forget to check out cuanto es 12500 pies en millas for an interesting conversion calculation. But remember, the cell cycle labeling answers key is just a hop away, so don’t miss out on that either!
There are a variety of labeling techniques that can be used to study the cell cycle. Each technique has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of technique will depend on the specific research question being asked.
Fluorescent Dyes
Fluorescent dyes are one of the most commonly used labeling techniques for studying the cell cycle. These dyes are small molecules that emit light when they are excited by a specific wavelength of light. By labeling cells with different fluorescent dyes, researchers can track the cells as they progress through the cell cycle and identify the stages at which they are arrested.
Fluorescent dyes are relatively easy to use and can be applied to cells in a variety of ways. However, they can be expensive and can sometimes interfere with the normal function of the cells.
Antibodies
Antibodies are proteins that are produced by the immune system in response to the presence of a foreign antigen. Antibodies can be used to label specific proteins within cells, and this can be used to study the expression and localization of proteins during the cell cycle.
Antibodies are highly specific and can be used to label a wide variety of proteins. However, they can be difficult to produce and can be expensive.
Genetic Labeling
Genetic labeling is a technique that uses genetic engineering to introduce a reporter gene into cells. The reporter gene encodes a protein that can be easily detected, such as a fluorescent protein or an enzyme. By introducing the reporter gene into cells, researchers can track the cells as they progress through the cell cycle and identify the stages at which they are arrested.
Genetic labeling is a powerful technique that can be used to study the cell cycle in great detail. However, it can be time-consuming and expensive to create genetically labeled cells.
Applications of Cell Cycle Labeling
Cell cycle labeling is a powerful technique used in both research and clinical settings to study cell proliferation, differentiation, and death. It involves the use of labeled nucleotides or antibodies to track cells as they progress through the cell cycle.
This information can be used to investigate a wide range of biological processes, including:
- Cell growth and development
- Tissue regeneration
- Cancer progression
- Response to therapy
Research Applications
In research, cell cycle labeling is used to study the dynamics of cell proliferation and differentiation. For example, researchers can use labeled nucleotides to track the rate at which cells enter S phase (DNA synthesis) and mitosis (cell division). This information can be used to investigate the effects of growth factors, hormones, and other signaling molecules on cell cycle progression.
Cell cycle labeling is also used to study the differentiation of stem cells into specialized cell types. By tracking the expression of specific genes and proteins, researchers can identify the molecular mechanisms that control cell fate decisions.
Clinical Applications
In clinical settings, cell cycle labeling is used to diagnose and monitor cancer. For example, the Ki-67 labeling index is a measure of the percentage of cells in a tumor that are actively proliferating. This information can be used to assess the aggressiveness of a tumor and to guide treatment decisions.
Cell cycle labeling is also used to monitor the response of cancer patients to therapy. By tracking the changes in the Ki-67 labeling index over time, doctors can assess the effectiveness of a particular treatment regimen.
Future Applications, Cell cycle labeling answers key
Cell cycle labeling has the potential to play an important role in future medical advancements. For example, it could be used to develop new therapies that target specific stages of the cell cycle. It could also be used to identify biomarkers that predict the response of cancer patients to therapy.
As our understanding of the cell cycle continues to grow, cell cycle labeling will become an increasingly valuable tool for both research and clinical applications.
Clarifying Questions: Cell Cycle Labeling Answers Key
What is cell cycle labeling?
Cell cycle labeling is a technique used to visualize and study the different stages of the cell cycle, the process by which cells grow and divide.
Why is cell cycle labeling important?
Cell cycle labeling allows researchers to track the progression of cells through the cell cycle, identify cell cycle abnormalities, and investigate the effects of various treatments on cell division.
What are the different cell cycle labeling techniques?
There are several cell cycle labeling techniques, including DNA labeling, antibody labeling, and fluorescent labeling, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.